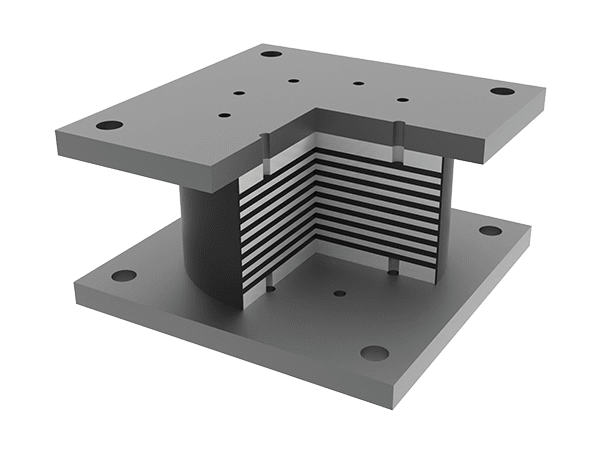
Round high damping rubber bearing
High damping rubber bearing, short for HDRB, is a kind of seismic isolation bearing that is much similar to natural rubber bearing in shape and structure. The difference between HDRB and NRB lies in that the HDRB offers better damping property by adding graphite filler (carbon black), reinforcing agent, vulcanizing agent, plasticizer and other compounding agents in natural rubber.
It not only maintains the good mechanical properties of natural rubber bearing, but also offers a high damping ratio, which allows the HDRB to absorb and dissipate the seismic energy in the earthquake, thus reducing the impact of the earthquake.
HDRB can be used in the seismic isolation systems separately and adjust the damping by regulating the amount of various compound agents added and the mixing ratio of these agents. Generally, damping ratio can reach up to 10% to 25%. Therefore, it is an economic and durable new seismic isolation device for buildings.
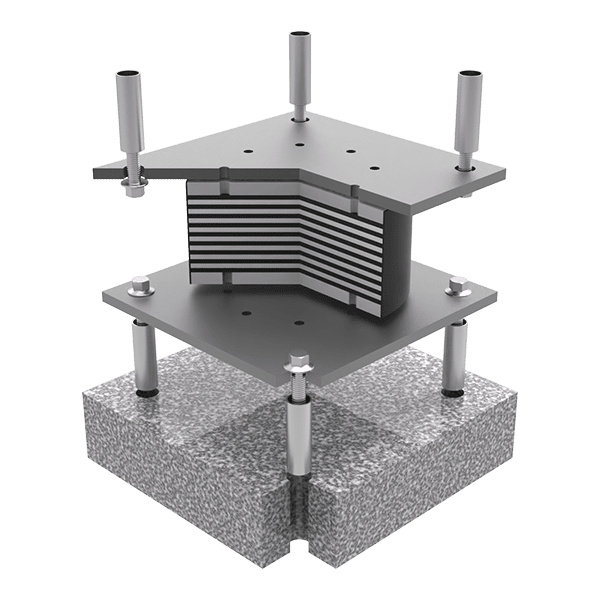
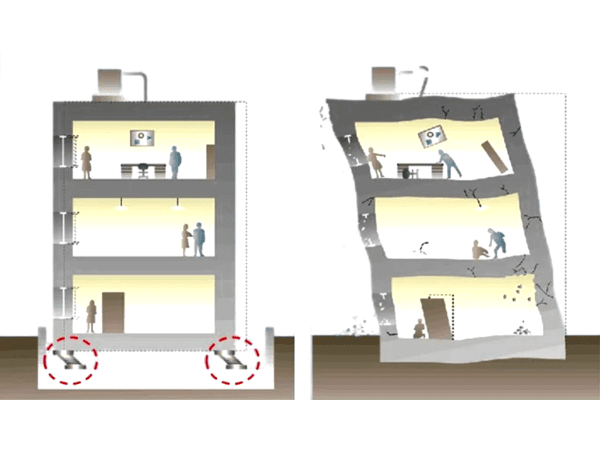
By introducing HDRBs in the structure, a soft seismic isolation layer is created to separate the superstructure from the lower foundation. In this way, it lowers the overall stiffness of the structure, extends its natural vibration period and reduces its natural vibration frequency, thus avoiding the highest frequency range of energy in the earthquake and reducing the input of seismic energy.
Meanwhile, the high damping characteristics of the seismic isolation layer ensure the absorption and dissipation of seismic energy and facilitate to reduce the response of the structure. In this way, the relative displacement will be concentrated in the seismic isolation layer with lower stiffness, thus limiting the upward transfer of seismic energy, and lowering the response of the superstructure.
When the earthquake comes, the vibration energy of the lower foundation is transferred to the high damping rubber bearing first. When the bearing is subject to a horizontal deformation, the HDRB offers certain resistances that can effectively absorb and dissipate seismic energy, to avoid or reduce the transmission of seismic energy to the upper structure, thus protecting the superstructure and personnel & equipment inside from earthquake damage.
After the earthquake, the bearing will restore to its original position through the recovery force of the rubber.
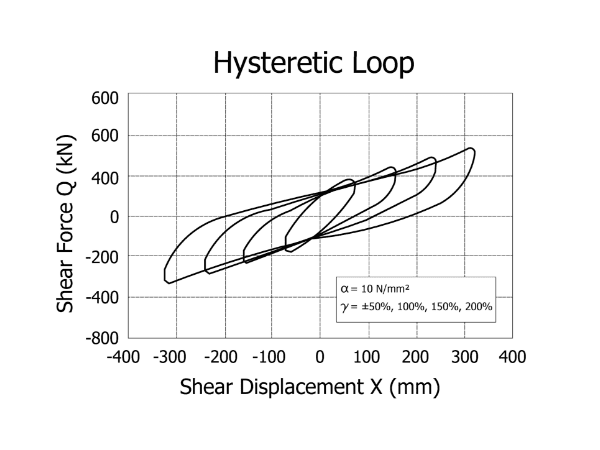
The curve shape is full, indicating that the HPRB has great energy dissipation capacity to ensure an amazing seismic isolation effect.
High damping rubber bearings are divided into round and rectangular high damping rubber bearings by shape.

Round high damping rubber bearing
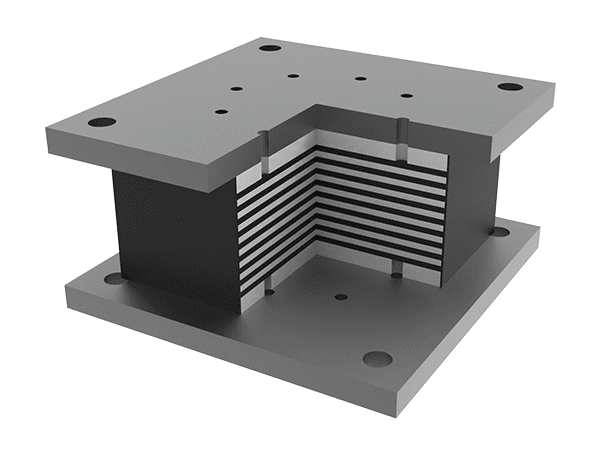
Rectangular high damping rubber bearing
High damping rubber bearing consists of top and a bottom connecting steel plates, internal high damping rubber layers, internal steel plates, a rubber cover and a top and a bottom sealing plates.
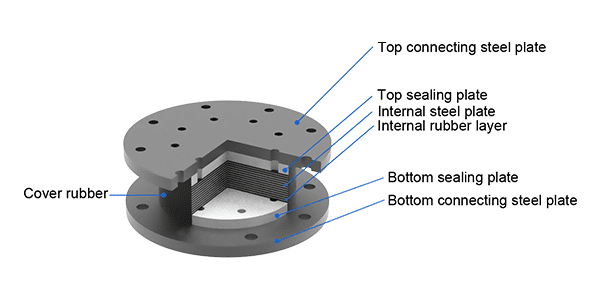
Round high damping rubber bearing structure

Rectangular high damping rubber bearing structure
| Item | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4 | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | HDRB (G4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ300 | Φ400 | Φ500 | Φ600 | Φ700 | Φ800 | Φ900 | Φ1000 | Φ1100 | Φ1200 | ||
| Shear modulus of elasticity N/mm2 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | |
| Vertical load (kN) | Fz | 500 | 1200 | 2200 | 2700 | 4000 | 5900 | 8800 | 10000 | 14000 | 16000 |
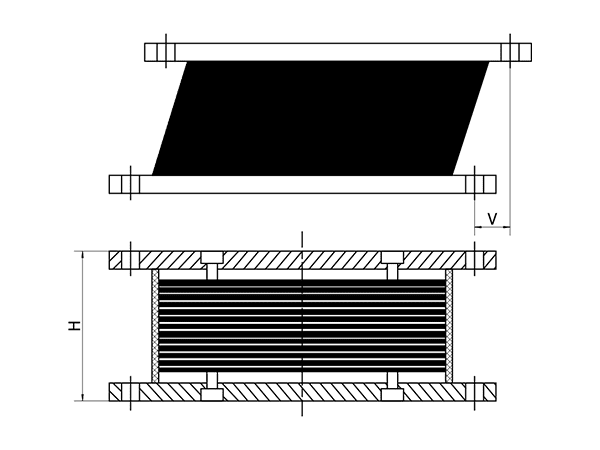
| Displacement (mm) | V | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Horizontal equivalent stiffness (kN/mm) | KH | 0.37 | 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 1.03 | 1.31 | 1.57 | 1.90 | 2.26 |
| Equivalent damping ratio (%) | Heq | 8–12 | |||||||||
| Dimension (mm) Te = rubber thickness |
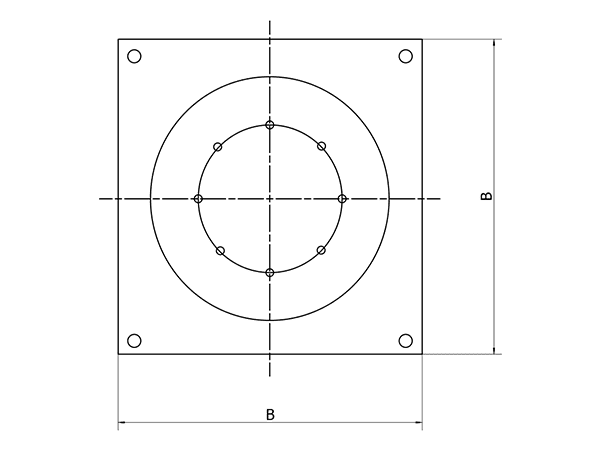
D | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 |
| H | 200 | 230 | 265 | 295 | 345 | 395 | 395 | 430 | 430 | 430 | |
| B | 350 | 450 | 55o | 650 | 750 | 850 | 950 | 1050 | 1150 | 1250 | |
| Te | 80 | 104 | 128 | 156 | 180 | 204 | 204 | 210 | 210 | 210 | |
| Notes: Other specifications are available upon request. |
|||||||||||
| Item | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | HDRB (G6) | |
| Φ300 | Φ400 | Φ500 | Φ600 | Φ700 | Φ800 | Φ900 | Φ1000 | Φ1100 | Φ1200 | ||
| Shear modulus of elasticity N/mm2 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical load (kN) | Fz | 500 | 1200 | 2200 | 2700 | 4000 | 5900 | 8800 | 1000o | 14000 | 16000 |
| Displacement (mm) | V | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Horizontal equivalent stiffness (kN/mm) | KH | 0.51 | 0.70 | 0.88 | 1.04 | 1.23 | 1.42 | 1.79 | 2.15 | 2.60 | 3.10 |
| Equivalent damping ratio (%) | Heq | 8–12 | |||||||||
| Dimension (mm) Te = rubber thickness |
D | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 |
| H | 200 | 230 | 265 | 295 | 345 | 395 | 395 | 430 | 430 | 430 | |
| B | 350 | 450 | 550 | 650 | 750 | 850 | 950 | 1050 | 1150 | 1250 | |
| Te | 80 | 104 | 128 | 156 | 180 | 204 | 204 | 210 | 210 | 210 | |
| Notes: Other specifications are available upon request. |
|||||||||||